
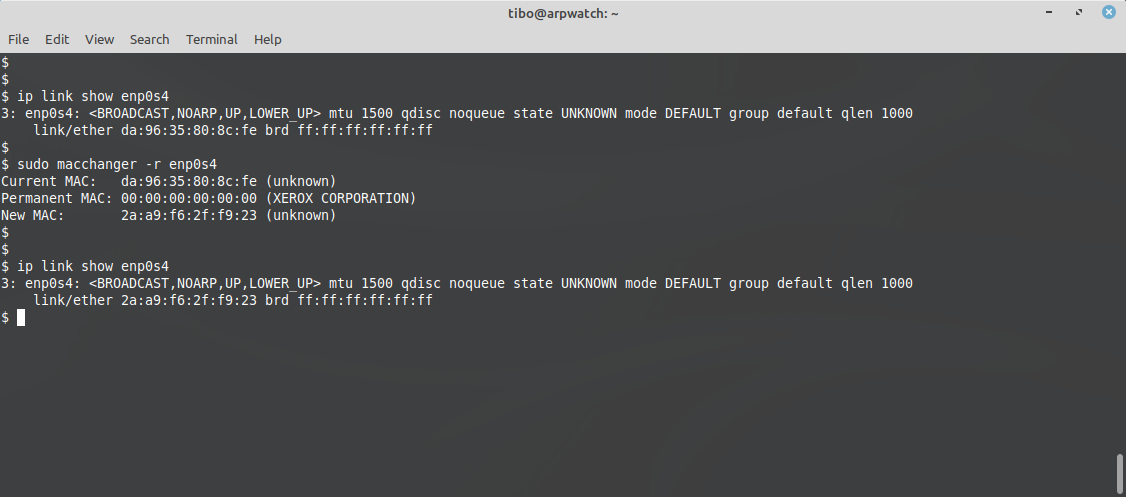
You'll have to manually change the modified address to the original MAC.īefore you can change the MAC address of your device using ip, you'll have to shut down the network interface. Once you've changed the MAC address using the below-mentioned commands, there's no option to revert to the original address automatically. You can effortlessly reset the changes back to default using the -p flag: sudo macchanger -p eth0 Using ip and ifconfig CommandsĪlthough macchanger is easy to use and well-suited for beginners, advanced Linux users who want more control over the operation might prefer using the ip command.īut first, make sure you note down the original MAC address of the interface before modifying it. With macchanger, you don't have to memorize the original MAC address of your device for future reference. To assign a custom MAC address to the eth0 interface: sudo macchanger -m 44:ee:bc:6c:76:ba eth0 where custom-address is the new MAC address you want to assign and interface is the name of the network interface. Basically, use the same command that you use for checking the IP address. It effectively asks “Who has this IP address?” This is a layer two message so it doesn’t rely on IP routing.Sudo macchanger -m custom-address interface Method 1: Find MAC address using command line There are serveral Linux networking commandsthat can be used to get the MAC address of the WiFi or LAN cards. When the router receives a packet for an IP address that isn’t in its table it sends a broadcast packet to the entire network.
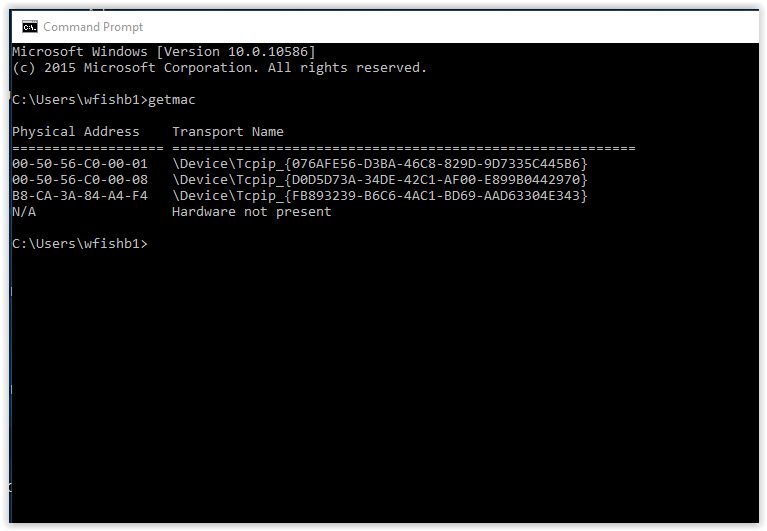
The radio waves used in Wi-Fi would also fall into this category. This is concerned with the physical infrastructure including cabling, routers, and network switches. 255), and then dump your arp table (arp -a on Linux), and you should find the MAC of the machine, along with its IP. It is used to send packets between directly-addressable devices using broadcasts to every device or unicasts to specific MAC addresses. The easiest way to do this is to ping the broadcast address (ping -b broadcast address) on your subnet (often. It’s the layer that the Internet Protocol-the IP in TCP/IP-operates at. This is where routing and packet forwarding takes place. The Transmission Control Protocol-the TCP in TCP/IP-operates at this layer. MAC Address stands for Media Access Control Address, which is a unique identifier assigned to any computers network interface. This layer is concerned with such things as transfer rates and data volumes. This is the layer that moves data around the network in a coordinated way. This layer involves itself with such matters as the initiation of a connection, handshaking, timeouts, and the breaking of connections that are no longer required. A session is a network connection between two or more devices. Encryption and decryption take place at this layer. This makes sure the data is in the right format or state as it moves to and from the network format. It provides information to the computer user and receives information back from them. Layer 7 is the top-most layer, the application layer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
